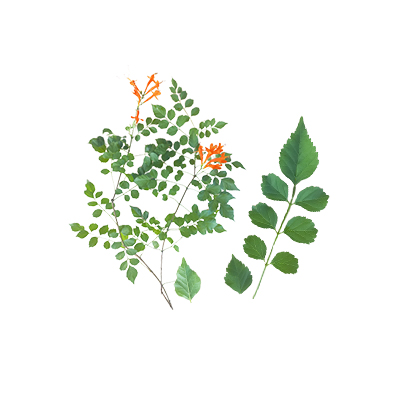
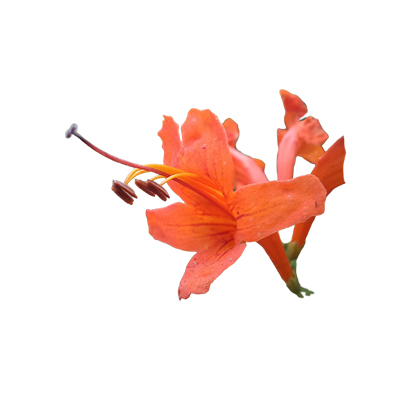
Cape Honeysuckle
Tecomaria capensis (Thunb.) Spach
Bignoniaceae
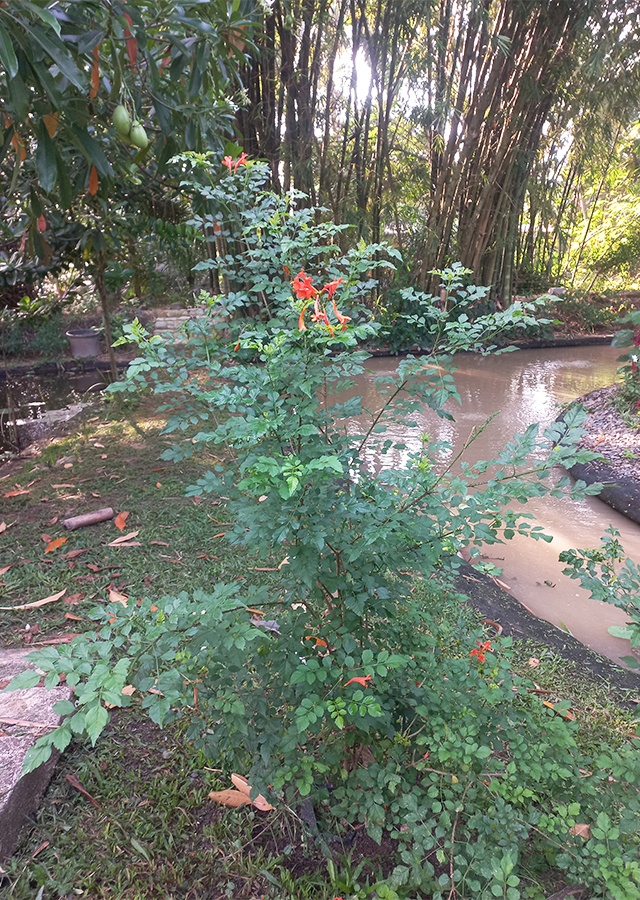
Location in our garden
Principal


Synonym
Bignonia capensis Thunb.
Gelseminum capense (Thunb.) Kuntze
Tecoma capensis (Thunb.) Lindl.
Habitus
Shrubs. An evergreen shrub or tree with a roundish crown - sometimes it develops a more or less climbing habit. It can grow from 0.5 - 10 m tall.
Part Used
Leaves
Bark
Flowers
Growing Requirements
Full Sunshine
Need Shade
Habitat
Forest
Coastal
Rocky Areas
Shrublands
Grassland
Terrestrial
Overview
Tecoma capensis is native to southern Africa (i.e., South Africa, Swaziland, and southern Mozambique). This plant is widely commercialized and cultivated as an ornamental plant in Europe, India, Singapore, Australia, tropical America, and islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It has various pharmacological activities, contains vitamins and minerals that help heal disease disorders in the body naturally. This plant is also used as a barrier plant, hedge and border plant, pioneer plant for new gardens, medicinal plant. Widely cultivated in tropical and warm climates in the world as ornamental plants and hedges. T. capensis is planted to protect the surrounding soil from erosion. This plant is harvested from the wild for local use as medicine and a fuel source. It is planted as a hedge or screen and is a valuable ornamental plant with a showy and abundant flowering display that attracts birds and insects.
Vernacular Names
Bejuco trompeta (Spanish), Jasmin du Cap (French), Trompetenwinde (German), Bignonia del Capo (Italy), Kaptrumpet (Swedish).
Agroecology
A plant of the subtropics to the tropics, where it can be found at elevations up to 2.300 m above sea level. It is found in areas where the mean annual rainfall is in the range 750 - 1.750 mm, and the mean annual temperature is within the range 22 - 26 °C. Mature plants can tolerate light frosts, quickly recovering from minor damage, but young plants are frost tender and should be protected during its first two cold seasons. Succeeds in full sun and in semi-shade. Grows in a variety of soils types. Prefers a well-drained, fertile soil with a pH of 5.5 - 6.5.
Morphology
- Stems - cylindrical, lenticellate, puberulous; cross section of the mature stem with peripheral phloem not forming a cross.
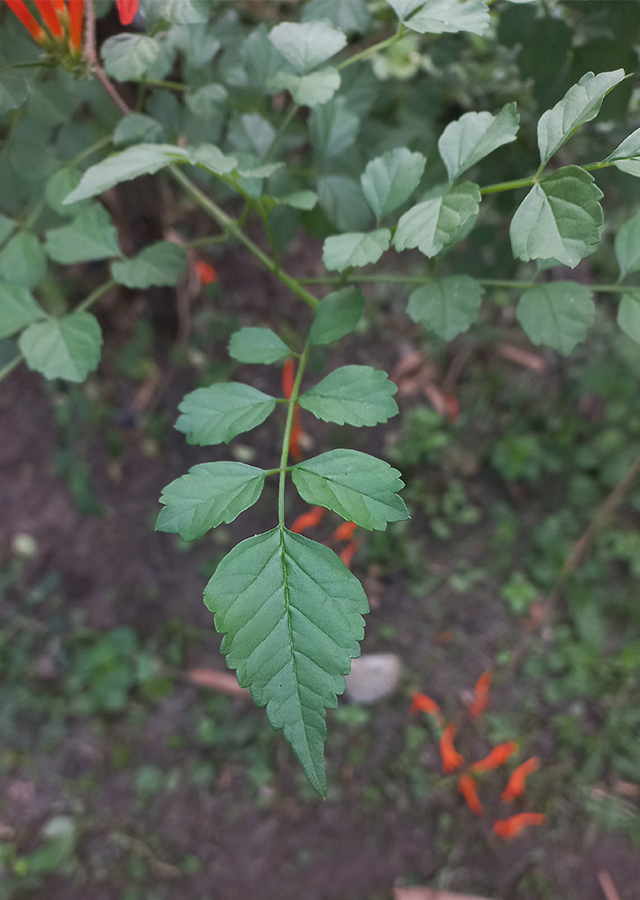
- Leaves - opposite, imparipinnate, 7-11-foliolate, without tendrils; leaflets 1.5-4.2 × 1-3 cm, elliptical to sub-rounded, membranaceous, sessile, the apex rounded, the base rounded or abruptly cuneate, the margins serrate; upper surface dull, pale, with slightly prominent venation; lower surface light green, dull, punctate, with slightly prominent venation, forming a conspicuous network, with tufts of hairs in the axils; petioles 1.5-2.5 cm long; pseudo-stipules absent.
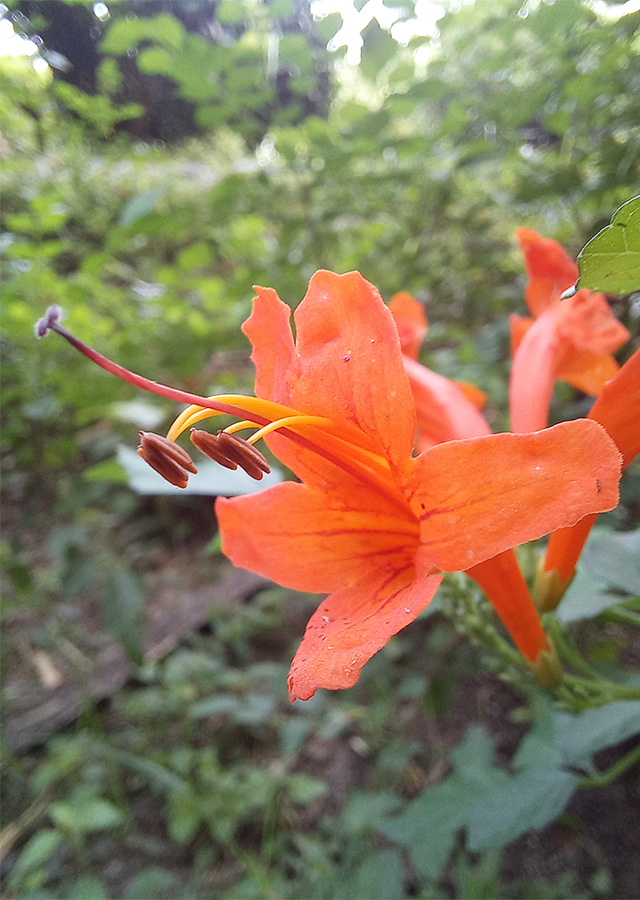
- Flowers - numerous in axillary racemes; pedicel 6-10 mm long. Calyx green, 5-7 mm long, 5-dentate, ciliate, puberulent; corolla orange or reddish orange, tubular, curved, 3.5-5 cm long, with 5 oblong, unequal lobes, the 2 upper lobes smaller than the 3 lower; stamens 4, of equal length; ovary superior, oblong, glabrous.
- Fruits - capsule linear, 5-11 cm long and 7-8 mm wide.
- Seeds - seeds in 2 rows, slender, 2-winged, the wings hyaline-membranaceous.
Cultivation
- Propagated by seed, cuttings of young wood, cuttings of half-ripe wood, layering.
- The branches often root where they touch the ground.
Chemical Constituents
Bioflavonoids, quercetin, essential oils, tannins, salicylic acid, iridoids, phenylpropanoid glucosides, tecomoside.
Traditional Medicinal Uses
- The powdered bark is used in the treatment of fevers, pneumonia and stomach troubles.
- The powdered bark is rubbed on bleeding gums to promote blood clotting.
- A leaf decoction is used in the treatment of diarrhoea and for intestinal inflammation. It is believed to ease pain and produce sleep.
Part Used
Reference Sources
- Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.Plants of the World Online: Tecomaria capensis (Thunb.) Spach. https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:111333-1. 24-02-2024.
- P Neelimaraj, P Srinivasa Babu, R Karthikeyan. 2015. Cape-honeysuckle: An Ornamental Plant to Treat Various Disease Conditions. Inventi Rapid: Planta Activa, 2015(3):1-5.
- Flora Fauna Web. Tecomaria capensis (Thunb.) Spach. https://www.nparks.gov.sg/florafaunaweb/flora/2/4/2498. 24-02-2024.
- Tropical Plants Database, Ken Fern. Tecoma capensis. https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Tecoma+capensis. 24-02-2024
- CABI. 2016. Tecoma capensis (Cape honeysuckle). https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.1079/cabicompendium.52954. 24-02-2024


