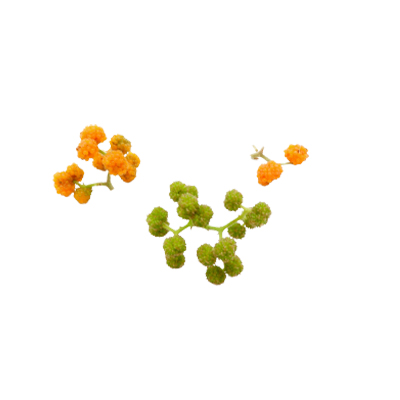Orange Wild Rhea
Debregeasia longifolia (Burm.f.) Wedd.
Urticaceae
Location in our garden
Principal



Synonym
Trema lancifolium Ridl.
Debregeasia angustifolia C.B.Rob.
Leucocnide affinis Miq.
Habitus
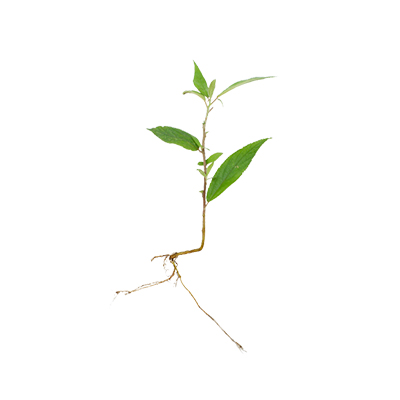
Shrubs. An evergreen shrub or small tree with slender stems, it can grow from 2 - 7 m tall
Part Used
Leaves
Fruit
Roots
Growing Requirements
Low Temperature
Habitat
Riverbanks
Forest
Overview
Debregeasia longifolia has a very wide distribution. Its distribution includes East Asia (China), the Indian subcontinent, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam, Malaysia, Indonesia, the Philippines. This species is taken from nature, mainly used as a source of high quality fiber obtained from the bark, but also as a food ingredient, drink (wine), medicinal plant, greenery, and ritual plant (India). In India, Pakistan, and even Indonesia, bark fibers are used to make ropes and fishing line. As a food ingredient, the leaves of Debregeasia longifolia have been used by the Karo Batak people (Indonesia) and the Garo tribe (India) as vegetables in their traditional dishes, and the fruit can be eaten directly. In Thailand, Debregeasia longifolia is planted as a pioneer species in a reforestation project to restore native forests. The species has also been classified as 'Least Concern' on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (2019). In addition, this species is also believed to have good health benefits, and has been used as traditional herbal medicine in China.
Vernacular Names
Khai plaa (Thai), Blaen-kee (Chiang mai).
Agroecology
Mainly found on old cultivated land, at elevations up to 2,100 m in the Himalayas. Also on moist places, especially in forests, along river-margins and on well-watered mountain sides, at elevations from 200 - 2,500 m. Debregeasia longifolia is a plant of low to moderate elevations in the tropics and subtropics. Plants can tolerate occasional lows to about -5 °C. Prefers a fertile well-drained loam with some shelter at the hottest part of the day.
Morphology
- Stems - slender, sometimes zigzagging from knot to knot. Bark is gray, smooth. The branches are round, slender, reddish brown or purplish, gray hairy.
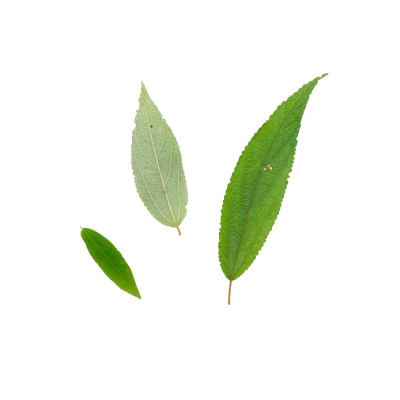
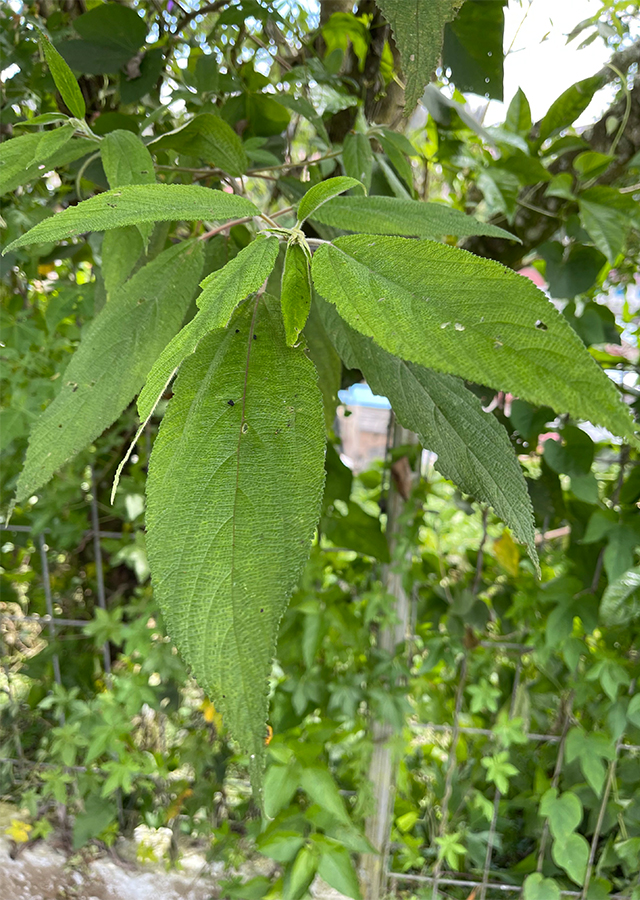
- Leaves - alternating (alternate), spiral, thin leaf blade, narrow oblong or lanceolate to oval or wide elliptical, often slightly asymmetrical, leaf base tapering to narrow round, serrate leaf edge, leaf tip pointed (acute) or tapering (acuminate), with 3 veins and (4-)5-6(-9) pairs of lateral veins. The upper leaf surface is rough, hairy, and green, while the lower surface is gray-green, thin hairy or gray-white tomentose. Gray hairy petiole.
- Flowers - like a knob. The flower heads are rounded, small, in the flowering phase bright red. The flower stalks are hairy like velvet. Inflorescences appear in the axilla, branched, with flowers in dense clusters, usually unisexual, rarely arranged with male bunches in the lower axillary and female bunches towards the apex and the middle in between. The male flower bunches are 3-5 mm in diameter, the female flower bunches are 1.5-2.5 mm in diameter. Male flowers with 4-5 perianth parts, oval tepals while female flowers with 4-branched or lobed perianth, linear stigma.
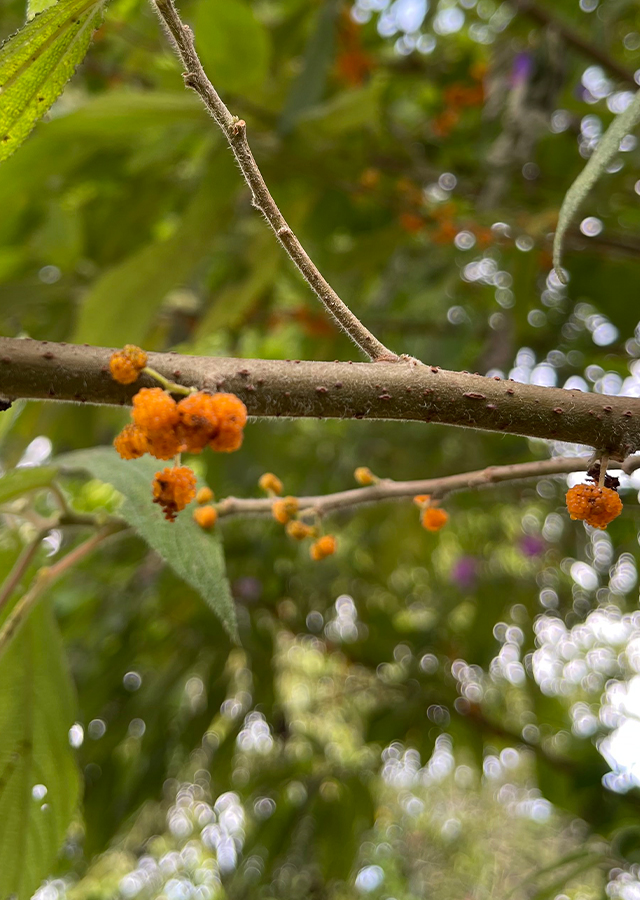
- Fruits - oblique ovoid or ovoid, achene slightly pressed to the side, rich in fiber. Ripe fruit is red, sour taste.
- Seeds - pods are orange-yellow when ripe.
Cultivation
- Propagated by seeds - in trays and only just cover the seed. Germination usually takes place within 1 - 2 months at 20 °C. When they are large enough to handle, prick the seedlings out into individual pots and plant them out when large enough.
- By soft-wood cuttings.
Chemical Constituents
Flavonoids (epicatechin, quercetin 3-O-#beta#-D-galactopyranoside, kaempferol 3-O-#beta#-D-galactopyranoside, quercetin 7-O-#beta#-D-glucopyranoside, apigenin 7-O-#beta #-D-glucopyranoside), a phenolic compound.
Traditional Medicinal Uses
- The juice of the leaves is applied to areas of the skin affected by scabies.
- The leaves are decocted with Pterocarya spp and used in the treatment of itch.
- Has activity as an antioxidant.
Part Used
Reference Sources
- Royal Botanic Gardens. Plants of the World Online: Debregeasia longifolia (Burm.f.) Wedd.. https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:851412-1. 06-06-22.
- Plant Resources of South-East Asia. 2016. Debregeasia longifolia (PROSEA). https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Debregeasia_longifolia_(PROSEA). 06-06-22.
- Tropical Plants Database, Ken Fern. 2021. Debregeasia longifolia. http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Debregeasia+longifolia. 06-06-22.
- Qin Bo, Wang Hanqing, Zhu Dayuan. 2003. Investigation on the chemical constituents of Debregeasia longifolia. Natural Product Research and Development, 15(1):21-23. https://europepmc.org/article/cba/361087. 06-06-22.
- Purba E. P., Silalahi M. 2021. Edible plants of the Batak Karo of Merdeka District, North Sumatra, Indonesia. Ethnobotany Research & Applications 22:01.
- Flowers of India. Orange Wild Rhea. https://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Orange%20Wild%20Rhea.html. 06-06-22.