Red Butterfly Wing
Christia vespertilionis (L.f.) Bakh.f.
Fabaceae
Location in our garden
Principal


Synonym
Hedysarum vespertilionis L.f.
Lourea vespertilionis (L.f.) Desv.
Habitus
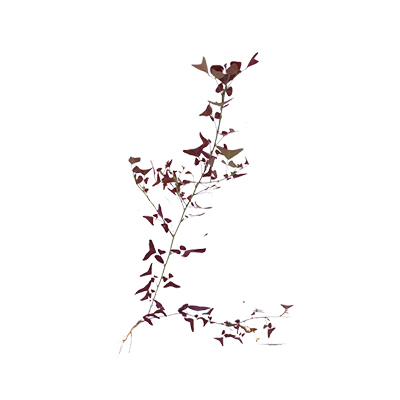
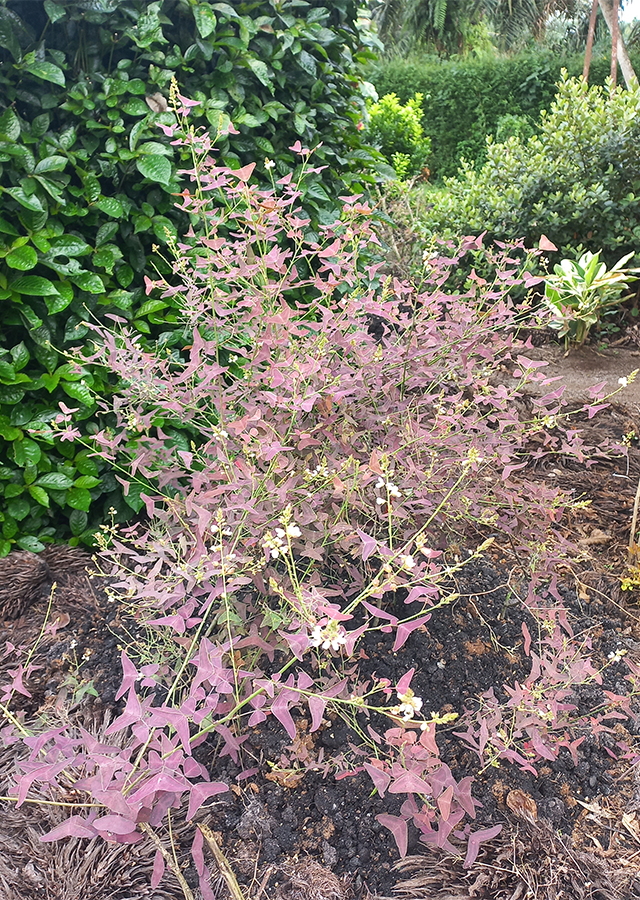
Herbaceous. A, slender, erect, sparingly-branched, herbaceous perennial plant with stems that can become more or less woody, It can grow 60 - 120 cm tall
Part Used
Leaves
The Whole Plant
Growing Requirements
Need Shade
Drought Resistant
Habitat
Terrestrial
Overview
Its native distribution is uncertain. Likely to be Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, Indonesia, China, and possibly Myanmar. The plant is harvested from the wild for local use as a medicine. It is grown as an ornamental, valued especially for its attractive leaves that look somewhat like a butterfly.
Vernacular Names
No found data on this. Need further research.
Agroecology
Grows on open grasslands, thickets, roadsides, seasides in southern China. A weed of pastures and roadsides, growing on sandy, gravelly and shale soils at elevations from 90 - 750 in Jamaica. The plant grows on lighter soils in the wild.
Morphology
- Roots - taproots, branched, cylindrical, dark yellow, also has small lateral roots.
- Stems - erect, green, cylindrical, slender and pubescent.
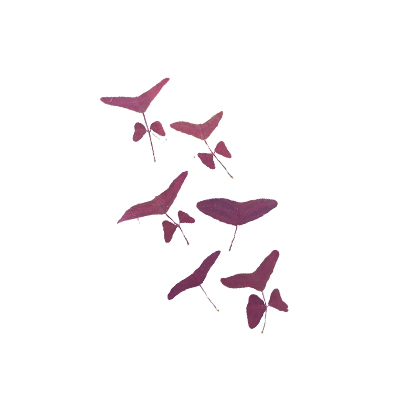
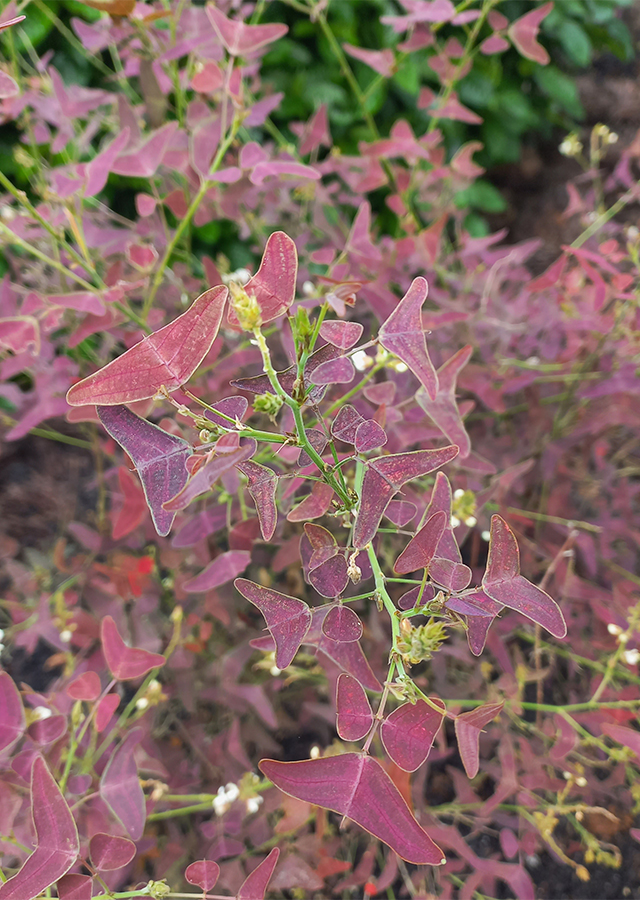
- Leaves - compound with 3 leaflets; and purplish red with stripes. Larger than the two lateral leaflets, the terminal leaflet is shaped like a boomerang. Leaves become bend downwards when night falls.
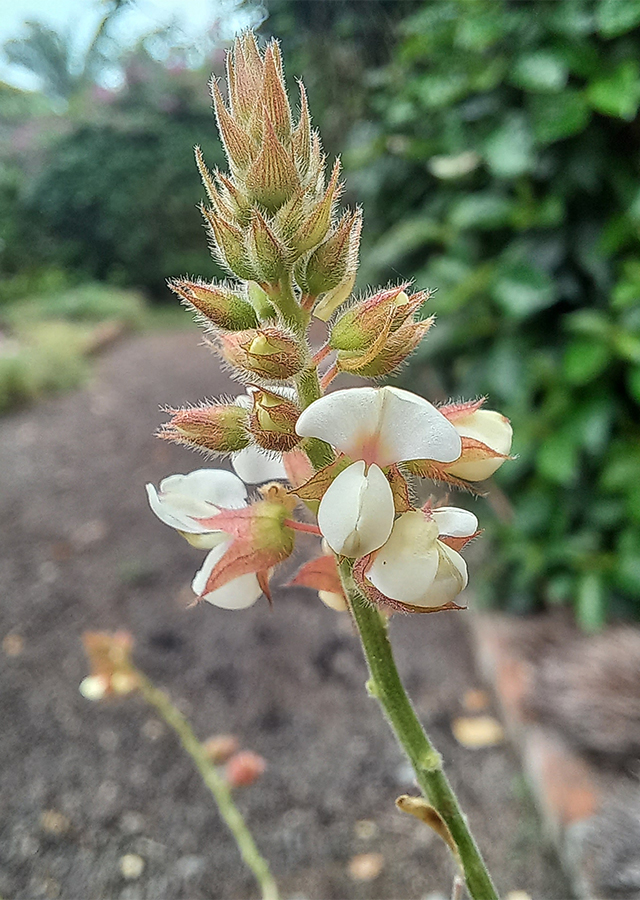
- Flowers - Inflorescences are 5 – 15 cm long with hairy pedicels. Flowers are off-white and about 6 mm in diameter. Calyx is reticulate veined. Upper 2 lobes of calyx are connate and lower lobes are almost as long the tube.
- Fruits - The legume is 4-or 5-jointed. Matured seeds are blackish brown, about 3 mm x 2mm. Seeds are glabrous and wholly enclosed by the calyx.
Cultivation
Propagated by seeds.
Chemical Constituents
Phenols, sterols, sesquiterpenoids, alkaloids, polyphenols, fatty acids, flavonoid glycosides, flavonols (quercetin, kaempferol), triterpenes, denbinobin, 5,7-dihydroxy-chromone, rhein, sanleng acid, wedelolacetone, phytol, 10-undecenoic acid, 6 -methylheptyl-2-propenoate, 2-(2-benzothiazolylthio)-1-(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)-ethanone, tetrahydro-2-methyl-thiophene, coumarins, tannins, quinine.
Traditional Medicinal Uses
- The whole plant is used medicinally for treating tuberculosis and snake bites.
- The leaves are used as a topical treatment for healing bone fractures.
Part Used
Reference Sources
- Fern, Ken. Useful Tropical Plants. (2021). Christia vespertilionis. http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Christia+vespertilionis. 05-01-22
- Flora & Fauna Web. Christia vespertilionis. https://www.nparks.gov.sg/florafaunaweb/flora/1/8/1811. 05-01-22

