Rose Apple
Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston
Myrtaceae
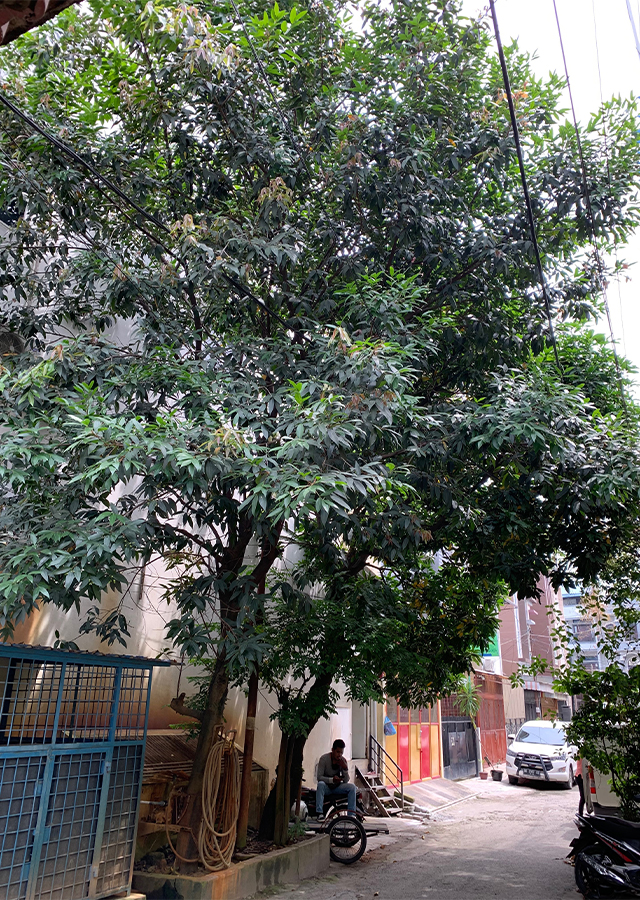
Location in our garden
Orchard



Synonym
Eugenia decora Salisb.
Eugenia jamboides Wender.
Eugenia jambos L.
Habitus
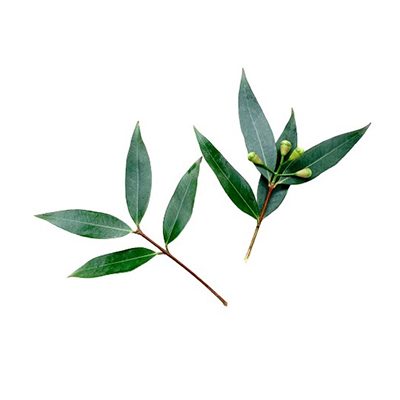
Trees. An evergreen tree with, dense crown of wide-spreading branches, it can grow 6-10 m tall. It is a small tree with spreading branches, leaves, simple, opposite, lanceolate, narrowed into short petioles, secondary nerves joined by a prominent looping intramarginal vein.
Part Used
Leaves
Seeds
Bark
Flowers
Fruit
Roots
Growing Requirements
Full Sunshine
Need Shade
Habitat
Riverbanks
Forest
Overview
It is found from Himalaya, but its exact origin is uncertain. It has been introduced and cultivated in home gardens elsewhere in the tropics and subtropics for its edible fruit, but also as ornamental or shade tree and wind-break. Today, the plant is cultivated in most tropical countries, including the Indian subcontinent and the sub-Saharan African regions.
Vernacular Names
Jambu mawar (Indonesia), Jamboes (Afrikaans), Yambo (Argentina), Pu ta (Chinese), Pome rose (French), Golapi-jamuk (India), Futo momo (Japanese), Chompu-nam dok mai (Thai).
Agroecology
Flourishes in tropical, usually below elevations of 1,200 m but up to 2,300 m in Ecuador. In dry areas, but fruits best in more humid regions. It grows best in temperatures are within the range 18-38 °C, but can tolerate 5-40 °C. Prefers a pH in the range 5.5-7, tolerating 5 - 8. It prefers a mean annual rainfall in the range 1,200-1,600 mm. Succeeds in any reasonable soil in full sun or part day shade.
Morphology
- Roots - tap roots.
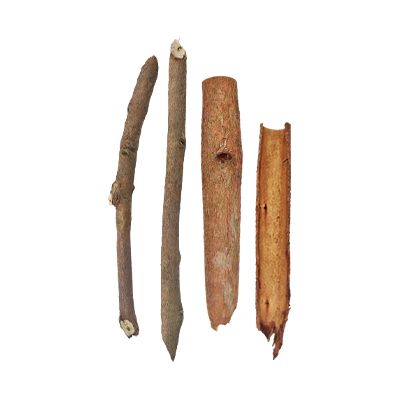
- Stems - tall 30 cm with flaky brown of barks.
- Leaves - narrow and glossy. thin, lanceolate, coriaceous, spanning a length of 10 cm to 23 cm, with along acuminate apex, cuneate base, and petioles measuring 0.5 to 1 cm in length.
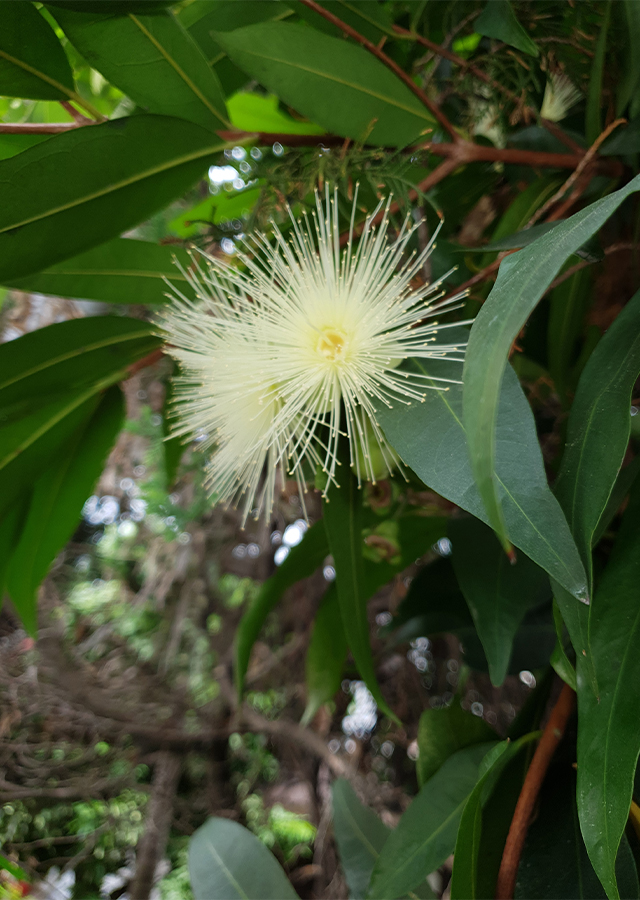
- Flowers - greenish-white or creamy-white, 5-10 cm in width, 7.5-10 cm in diameter.
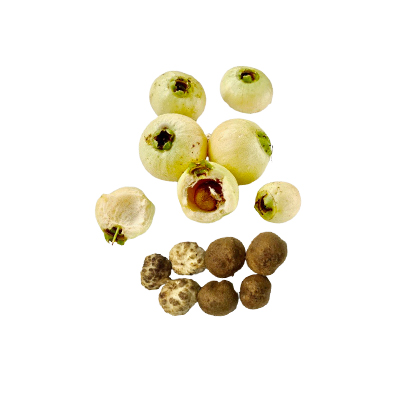
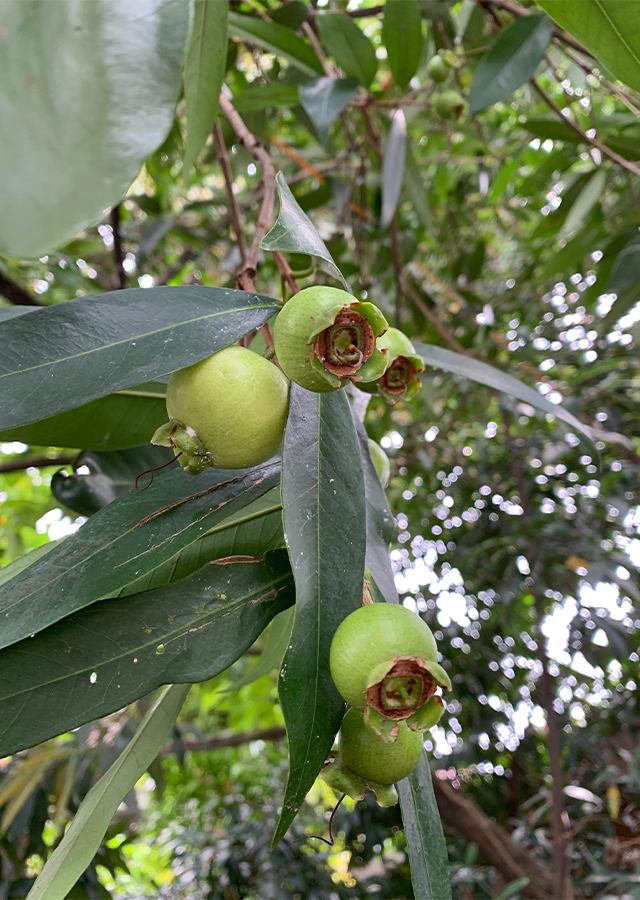
- Fruits - bell-shaped, length: 5–8 cm with pink-red fruit, flesh color is white, the taste is mild sweet. Fruit season in early winter to late fall.
- Seeds - 1 or 2 in each fruit, grey.
Cultivation
- By seeds - the seeds have a very short viability and no dormancy; they usually germinate well within 10-120 days if sown fresh.
- Young plants transplant badly, so should be potted up into individual containers as soon as they are large enough to handle and before the roots have grown much.
- Propagated also by air layering and cutting.
Chemical Constituents
Tannin, alkaloid, polifenol, essential oil, squalene, ursolic acid, myricetin, myricitrin, gallic acid, salicylic acid, anacardic, anthraquinones, steroid, triterpene, saponin, Friedelin, Amyrin acetate, Betulinic acid, Lu peol, Friedelolactone, Friedelano.
Traditional Medicinal Uses
Medicinal Uses
- Several parts of the tree have several biological activity suuch as diureticactivity, Antifungal activity, Antidermatophytic activity, Antibacterial activity, Antibiotic-modulating activity, Hepatoprotective agent, Analgesic effects, Anti oxidant ,anti inflammatory, anti diabetic, anticancer, anti ulcer, anti pyretic, cardio vascular diseases, anti hyperlipidimic and neurological disorders like alzheimer’s, and anti parkinsonism.
- It is rich in vitamin C which prevents the damage of free radicals, pollutants and toxic chemicals which leads to the health ailments such as heart disease, cancer and arthritis.
- Reduced risk of stroke, boost good HDL cholesterol, prevent diabetes, prevent constipation, acne, prevents muscle cramping, skin health, antimicrobial, cure leaver damage.
- Flowers have antipyretic effects and seeds treat dysentery, diarrhea and catarrh.
- Bark is used to treat asthma and bronchitis.
Traditional Uses
- The root is used by the people of Cuban to treat epilepsy.
- Fruit peel strengthens spleen, warm stomach, treat deep ulcers, tumors.
- The decoction made from astringent bark is used in folkloric medicine in Malaysia to treat thrush.
- In China, root bark and fruit are used as a blood coolant.
- The decoction made from the leaves acts as an expectorant and diuretic which treats rheumatism and also cures the sore eyes.
- In India, the fruit is used as a tonic to enhance the liver and brain.
- The health conditions such as dysentery, catarrh and diarrhea could be treated with the use of seeds. In Nicaragua an infusion of roasted and powdered seeds is used to treat diabetes. In Colombia, people believe that the seeds possess pain killer properties.
Part Used
Reference Sources
- Fern, Ken. (2014). Useful Tropical Plants. Rose Apple Syzygium jambos. http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Syzygium+jambos. 02-02-2021.
- Health Benefits Times Database. (No date). Rose Apple Syzygium jambos. https://www.healthbenefitstimes.com/watery-rose-apple. 02-02-2021.
- Hindawai. (2018). Syzygium jambos Displayed Antibacterial and Antibiotic-Modulating Activities against Resistant Phenotypes. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2018/5124735/. 02-02-2021.
- Lim, T.K. (2016). Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants. New York. Springer Vol. 3 page 730.
- Jahan N. 2019. A Review Study on Ethnopharmacological & Phytochemical Comparison Between Syzygium cumini & Syzygium jambos of Genus Syzygium (Family: Myrtaceae). World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences 5(6).