Nipa palm
Nypa fruticans Wurmb
Arecaceae
Location in our garden
Orchard



Synonym
Cocos nypa Lour.
Nipa arborescens Wurmb ex H.Wendl.
Nipa litoralis Blanco
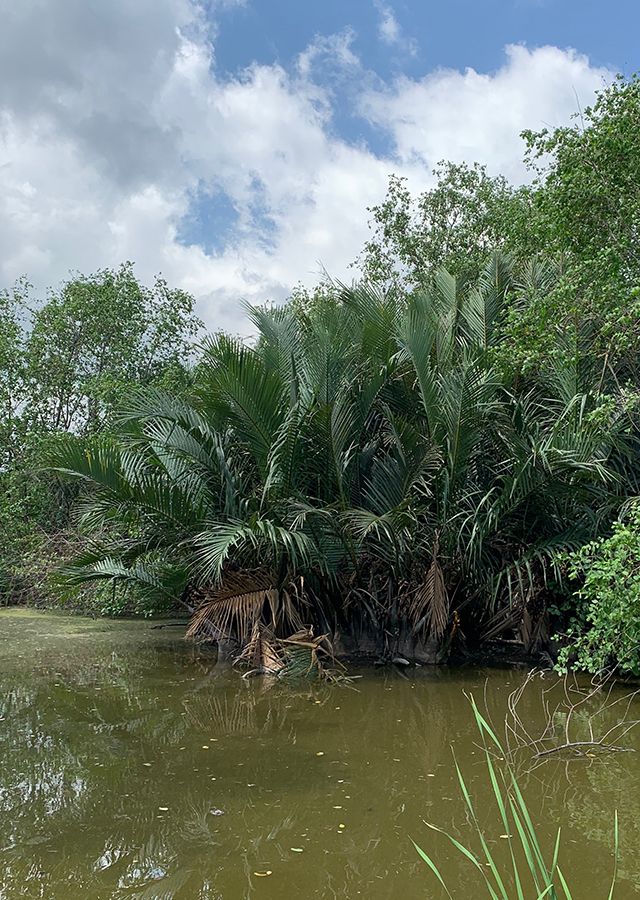
Habitus
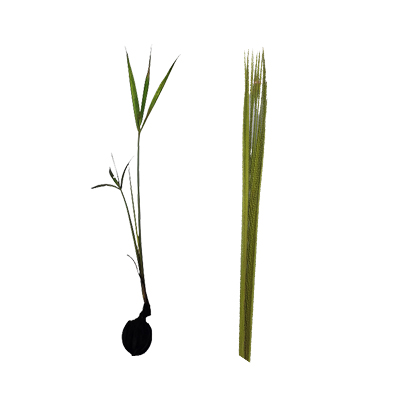
Palm. An estuarine clumping palm, perennial, growing up to 10 m
Part Used
Shoots
Leaves
Seeds
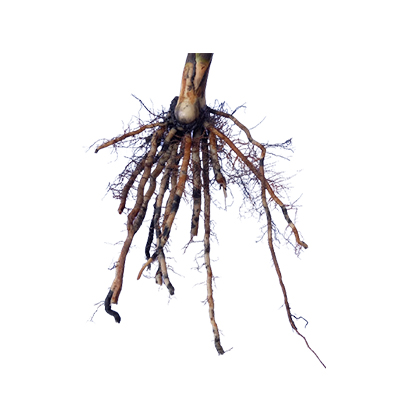
Roots
Sap
Growing Requirements
Full Sunshine
Habitat
Wetland
Coastal
Overview
Interesting to note that this plant is one of the oldest angiosperm plants and possibly the oldest palm species. Some fossil findings suggest that it had a pantropical distribution 13-63 million years ago. Nevertheless it is presumably native to South Asia (Sri Lanka, Bangladesh,India), South-East Asia, Northern Australia and to the Pacific Islands (Solomon, Marianas, Caroline islands). It was introduced to West Africa in the beginning of 20th century and is found in Nigeria and in Cameroon. Today it is mainly found in Indonesia (700,000 ha), Papua New Guinea (500,000 ha) and the Philippines (8000 ha).
Vernacular Names
Golpata (Bangladesh), Gin-pol (Sri Lanka), Nipah (Malaysia), Biri- biri (Koriki-Papua New Guinea), Rola (Australia), Ayamatangh (Nigerian), Lasa (Tagalog-Philippines) Nipah (Indonesia), Nipa palm (English), Palmier Nipa (French), Dane (Myanmar), Dừa nước, Dừa lá (Vietnam)
Agroecology
Nipa palm is tropical palm and needs a minimum temperature of 20 °C and maximum of 32–35 °C. It is fond of subhumid to humid climate with more than 100 mm rainfall per month. It thrives only in slow moving tidal, brackish water in which the soil is muddy and rich in alluvial silt, clay and humus. This kind of soil contains high concentration of various inorganic salts such as calcium, and sulphides of iron and manganese.
Morphology
- Stems - subterranean horizontal stem (rhizome) that grows beneath the ground; up to 45 cm in diameter, branching dichotomously at regular intervals, with curved leaf scars above, and roots along the underside
- Leaves - stiffly erect, up to 1.5 m long, simply pinnate, two ranked, leaflets up to 163 per leaf and midrib has appressed brown scales on lower surface.
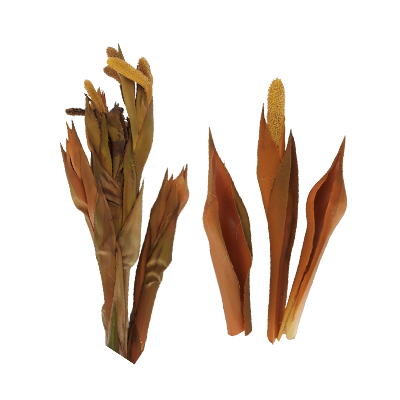
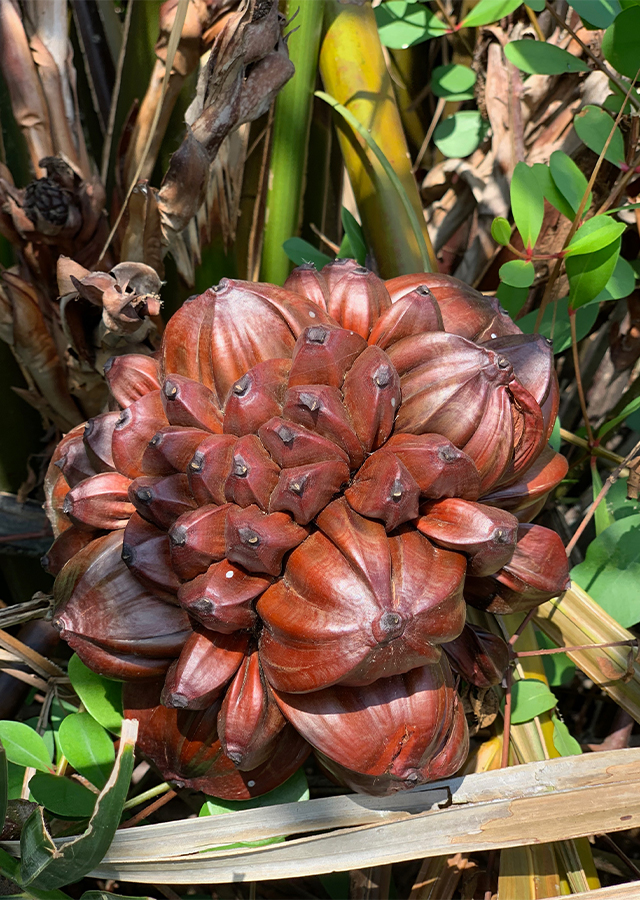
- Flowers - dimorphic, monoecious, male flowers with 3 stamens, filaments united into a column, without pistillodes; female flowers without staminodes; 3 distinct carpels (pistils), much longer than perianth, irregularly polyhedric, curved and angled, with a funnel-shaped stylar opening.
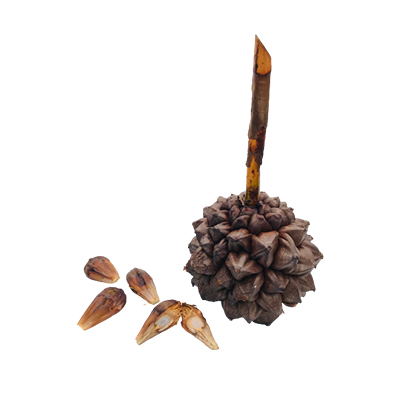
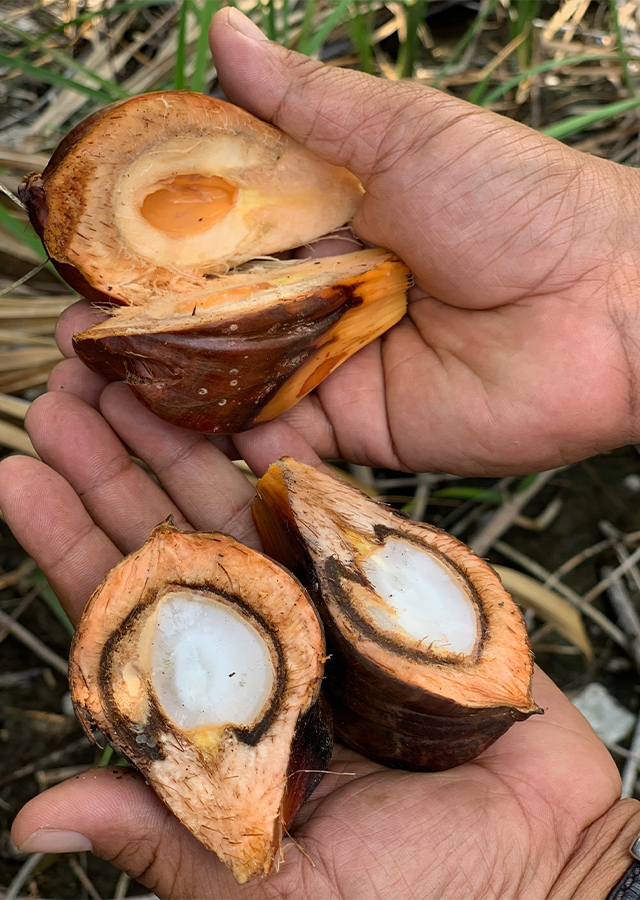
- Fruits - a drupe, up to 40 cm in diameter, developing from 1 carpel, pyramidal, brown to blackish in color, exocarp smooth, mesocarp fibrous, endocarp thick and composed of interwoven fibrous strands.
- Seeds - broadly ovoid with homogenous endosperm or rarely ruminate, with a central hollow; embryo basal
Cultivation
It is sexually propagated using its seeds and asexually by its dichotomous branching of the rhizome. People in Papua New Guinea have been successfully propagate nipa using a method called “pocket and channel” where its fruits is placed directly into 10-20 cm deep pockets along the edge of irrigation channels.
Chemical Constituents
Stigmasterol, sitosterol, β-sitostenone, stigmasta-4,22-dien-3-one, daucosterol, diosgenin, and dioscin.
Traditional Medicinal Uses
- Use for treatment of ulcers, diabetes, herpes, headache, toothache, and blackening teeth, inflammations of eyelids and conjunctiva.
- In Malaysia, juice from the shoots is mixed with coconut milk for treating herpes and the residue pulp is applied on the infected skin.
- The ash from burnt leaves and roots gives an ash-salt called "garam nipah" which is used for headache and toothache in Borneo.
- In Philippines, the decoction of fresh leaves is used as a lotion for indolent ulcers.
- Traditional healers of Karo, Indonesia use the plant for treatment of diabetes.
Part Used
Reference Sources
- Flach, M. & Rumawas, F. (Editors), 1996. Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 9. Plants yielding non-seed carbohydrates. Prosea Foundation, Bogor, Indonesia. 237 pp.
- Si, Z. 2008. Studies on the chemical constituents of Nypa fruticans. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs.
- http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:31397-1