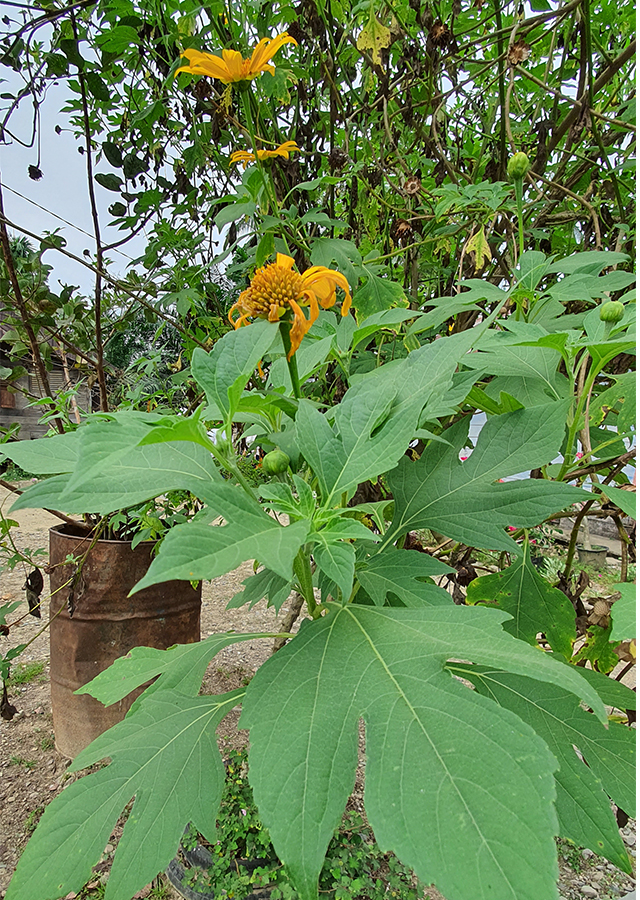
Mexican Sunflower
Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsl.) A.Gray
Asteraceae
Location in our garden
Principal
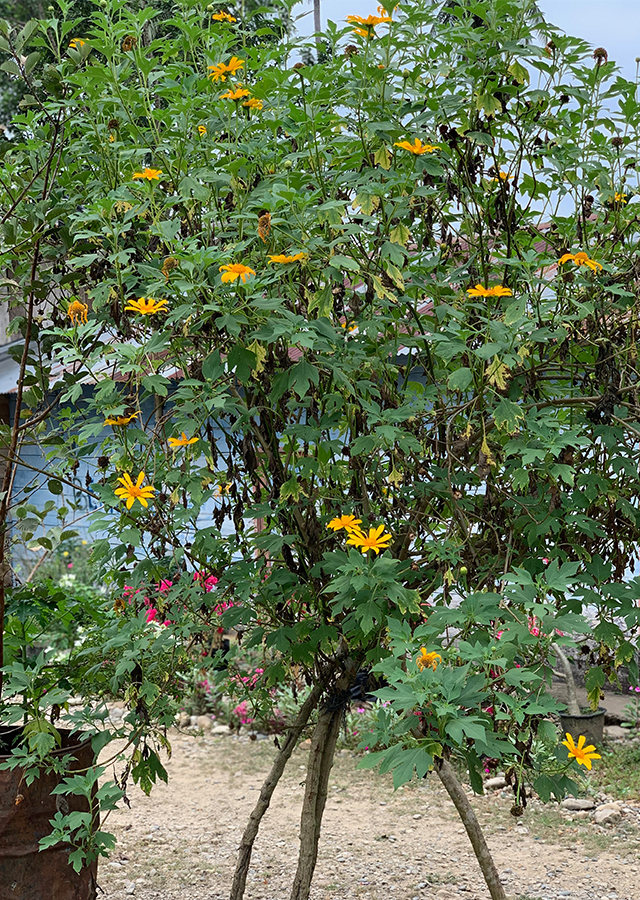


Synonym
Helianthus quinquelobus Sessé & Moc.
Mirasolia diversifolia Hemsl.
Tithonia diversifolia subsp. glabriuscula S.F.Blake
Habitus
Shrubs. A robust plant that grows up to 3 m tall.
Part Used
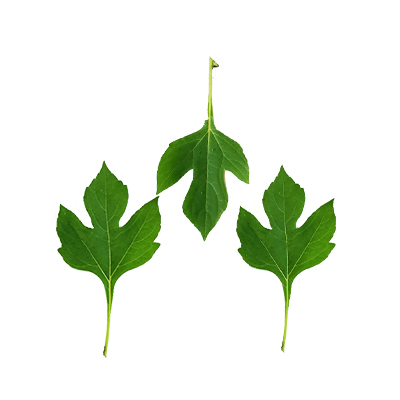
Leaves
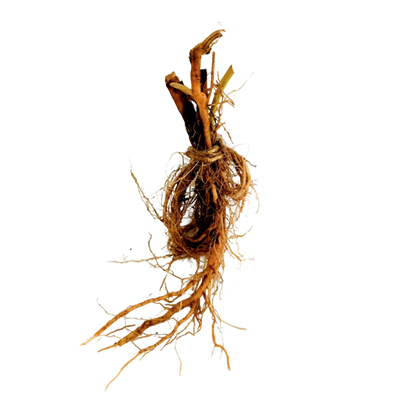
Roots
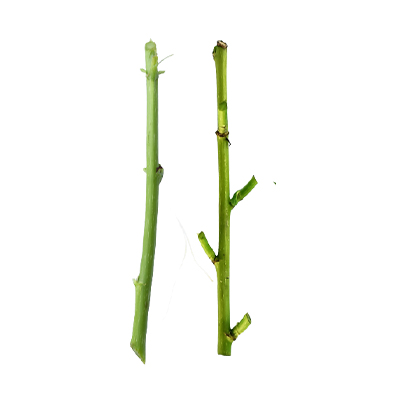
Stem
Growing Requirements
Full Sunshine
Drought Resistant
Habitat
Riverbanks
Roadside
Shrublands
Grassland
Overview
Mexican sunflower is native to Mexico and Central America. It has been widely introduced throughout tropical and subtropical regions of the world and it can now be found cultivated and naturalized across South America, the West Indies, Africa, Asia, Australia, and on many islands across the Pacific and the Indian Ocean. It is harvested from the wild for local use as medicine and fuel.
Vernacular Names
Campana (Mexico), Girasol mejicano (Puerto Rico), Daoruang-yipun (Thailand), Japanese sunflower (Japan), Verschiedenblaettrige Fackelblume (German).Wang ye kui (Chinese).
Agroecology
T. diversifolia prefers to grow where mean annual temperatures range from 15-31 °C but it can tolerate temperatures from 12-38 °C. It prefers environments with a mean annual rainfall in the range from 1000 mm to 2,000 mm although it tolerates rainfall from 700 mm to 2,500 mm. This species is adapted to grow in a wide range of soil types including sandy, loamy, and clay soils with a pH range of 6.1-7.8 pH. This species prefers open and sunny areas and can tolerate moderate drought events
Morphology
- Roots - taproot with many fine secondary roots.
- Stems - branches are stout, almost glabrous. Stems are hollow, slightly ridged.
- Leaves - greyish green, alternate, petioled, membranaceous, ovate to orbicular, 2 to 10 cm long, entire or 3- to 5-lobed, finely hairy, with toothed margins.
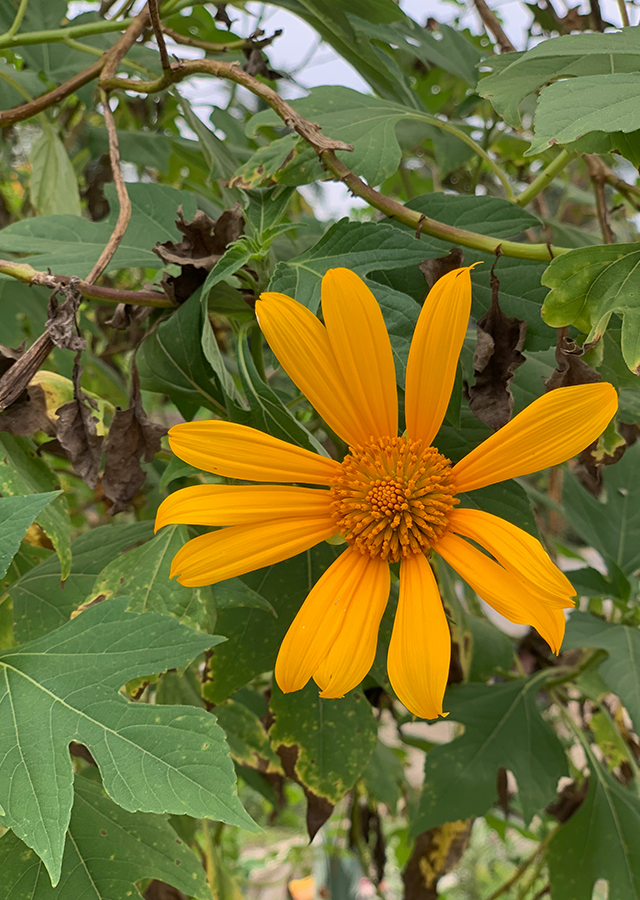
- Flowers - yellow, large, daisy-like, on peduncles 7 to 30 cm long. Petals are 7 to 15, bright yellow, 4 to 7 cm long, and 9 to 16 mm wide, with three small teeth at the tips. The Center of the flower heads has about 80 to 120 tiny tubular florets surrounded by several rows of green bracts.
- Seeds - 4 to 8 mm long and topped with a ring of scales and two awns, blackish in color, and somewhat four-angled.
Cultivation
Propagated by seed-sow in situ.
Chemical Constituents
Phenol, chlorogenic, flavonoids, alkaloids, sesquiterpenoid lactone (caryophyllene, copaene, bicyclogermacrene, juniper camphor) saponins, tannins, tagitinin C, tirotundin, polyphenol, caffeic acid, ascorbic acid.
Traditional Medicinal Uses
- Considered antimalarial, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-diarrheal, anti-spasmodic, vasorelaxant, chemopreventive.
- Studies have suggested antimicrobial, analgesic, antidiabetic, hepatoprotective, repellent, antiemetic, radical scavenging.
- An ethanol extract of the leaves showed a reduction of blood glucose levels, and also significantly lowered plasma insulin, decreasing blood glucose in an insulin tolerance test.
- In Africa, the infusion is used for constipation, indigestion, sore throat.
- The leaves are used for the treatment of stomach pains, liver pains, indigestion and as an antiviral
- In Mexico, used for the treatment of malaria, hematomas, and muscular pain.
- In Taiwan, used for diabetes.
- In Kenya, used for malaria and as an antidote for snakebite, and to treat ectoparasites in cattle
Part Used
Reference Sources
- CABI. (2014). Invasive Species Compendium: Tithonia diversifolia (Mexican sunflower). https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/54020#07BD8BD4-DDD7-4D33-B52D-491E04B7F2ED. 06-02-2021.
- Fern, Ken. (2014). Useful Tropical Plants: Tithonia diversifolia. http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Tithonia+diversifolia. 06-02-2021.
- Stuart Xchange. (2015). Philippinee Medicinal Plants: Wild sunflower Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsl.) A. Gray. http://stuartxchange.com/WildSunflower. 06-02-2021.


